延时任务的四种实现方式
什么是延迟任务?
顾明思议,我们把需要延迟执行的任务叫做延迟任务。
延迟任务的使用场景有以下这些:
红包 24 小时未被查收,需要延迟执退还业务;
每个月账单日,需要给用户发送当月的对账单;
订单下单之后 30 分钟后,用户如果没有付钱,系统需要自动取消订单。
等事件都需要使用延迟任务。
延迟任务实现思路分析
延迟任务实现的关键是在某个时间节点执行某个任务。基于这个信息我们可以想到实现延迟任务的手段有以下两个:
自己手写一个“死循环”一直判断当前时间节点有没有要执行的任务;
借助 JDK 或者第三方提供的工具类来实现延迟任务。
而通过 JDK 实现延迟任务我们能想到的关键词是:DelayQueue、ScheduledExecutorService,而第三方提供的延迟任务执行方法就有很多了,例如:Redis、Netty、MQ 等手段。
延迟任务实现
限循环实现延迟任务
此方式我们需要开启一个无限循环一直扫描任务,然后使用一个 Map 集合用来存储任务和延迟执行的时间,实现代码如下:
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;/*** 延迟任务执行方法汇总*/
public class DelayTaskExample {// 存放定时任务private static Map _TaskMap = new HashMap<>();public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("程序启动时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());// 添加定时任务_TaskMap.put("task-1", Instant.now().plusSeconds(3).toEpochMilli()); // 延迟 3s// 调用无限循环实现延迟任务loopTask();}/*** 无限循环实现延迟任务*/public static void loopTask() {Long itemLong = 0L;while (true) {Iterator it = _TaskMap.entrySet().iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) it.next();itemLong = (Long) entry.getValue();// 有任务需要执行if (Instant.now().toEpochMilli() >= itemLong) {// 延迟任务,业务逻辑执行System.out.println("执行任务:" + entry.getKey() +" ,执行时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());// 删除任务_TaskMap.remove(entry.getKey());}}}}
} 以上程序执行的结果为:
程序启动时间:2020-04-12T18:51:28.188
执行任务:task-1 ,执行时间:2020-04-12T18:51:31.189
可以看出任务延迟了 3s 钟执行了,符合我们的预期。
2.Java API 实现延迟任务
Java API 提供了两种实现延迟任务的方法:DelayQueue 和 ScheduledExecutorService。
① ScheduledExecutorService 实现延迟任务
我们可以使用 ScheduledExecutorService 来以固定的频率一直执行任务,实现代码如下:
public class DelayTaskExample {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("程序启动时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());scheduledExecutorServiceTask();}/*** ScheduledExecutorService 实现固定频率一直循环执行任务*/public static void scheduledExecutorServiceTask() {ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 执行任务的业务代码System.out.println("执行任务" +" ,执行时间:" + LocalDateTime.now());}},2, // 初次执行间隔2, // 2s 执行一次TimeUnit.SECONDS);}
}以上程序执行的结果为:
程序启动时间:2020-04-12T21:28:10.416
执行任务 ,执行时间:2020-04-12T21:28:12.421
执行任务 ,执行时间:2020-04-12T21:28:14.422
......
可以看出使用 ScheduledExecutorService#scheduleWithFixedDelay(...) 方法之后,会以某个频率一直循环执行延迟任务。
② DelayQueue 实现延迟任务
DelayQueue 是一个支持延时获取元素的无界阻塞队列,队列中的元素必须实现 Delayed 接口,并重写 getDelay(TimeUnit) 和 compareTo(Delayed) 方法,DelayQueue 实现延迟队列的完整代码如下:
public class DelayTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {DelayQueue delayQueue = new DelayQueue();// 添加延迟任务delayQueue.put(new DelayElement(1000));delayQueue.put(new DelayElement(3000));delayQueue.put(new DelayElement(5000));System.out.println("开始时间:" + DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(new Date()));while (!delayQueue.isEmpty()){// 执行延迟任务System.out.println(delayQueue.take());}System.out.println("结束时间:" + DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(new Date()));}static class DelayElement implements Delayed {// 延迟截止时间(单面:毫秒)long delayTime = System.currentTimeMillis();public DelayElement(long delayTime) {this.delayTime = (this.delayTime + delayTime);}@Override// 获取剩余时间public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {return unit.convert(delayTime - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}@Override// 队列里元素的排序依据public int compareTo(Delayed o) {if (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {return 1;} else if (this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) < o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {return -1;} else {return 0;}}@Overridepublic String toString() {return DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance().format(new Date(delayTime));}}
}以上程序执行的结果为:
开始时间:2020-4-12 20:40:38
2020-4-12 20:40:39
2020-4-12 20:40:41
2020-4-12 20:40:43
结束时间:2020-4-12 20:40:43
3. 监听Redis过期key
在Redis中,有个发布订阅的机制

生产者在消息发送时需要到指定发送到哪个channel上,消费者订阅这个channel就能获取到消息。图中channel理解成MQ中的topic。
并且在Redis中,有很多默认的channel,只不过向这些channel发送消息的生产者不是我们写的代码,而是Redis本身。这里面就有这么一个channel叫做__keyevent@
当某个Redis的key过期之后,Redis内部会发布一个事件到__keyevent@
所以基于监听Redis过期key实现延迟任务的原理如下:
将延迟任务作为key,过期时间设置为延迟时间
监听__keyevent@
__:expired这个channel,那么一旦延迟任务到了过期时间(延迟时间),那么就可以获取到这个任务
实现代码如下:
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPubSub;
import utils.JedisUtils;public class TaskExample {public static final String _TOPIC = "__keyevent@0__:expired"; // 订阅频道名称public static void main(String[] args) {Jedis jedis = JedisUtils.getJedis();// 执行定时任务doTask(jedis);}/*** 订阅过期消息,执行定时任务* @param jedis Redis 客户端*/public static void doTask(Jedis jedis) {// 订阅过期消息jedis.psubscribe(new JedisPubSub() {@Overridepublic void onPMessage(String pattern, String channel, String message) {// 接收到消息,执行定时任务System.out.println("收到消息:" + message);}}, _TOPIC);}
}4. MQ 实现延迟任务
如果专门开启一个 MQ 中间件来执行延迟任务,就有点杀鸡用宰牛刀般的奢侈了,不过已经有了 MQ 环境的话,用它来实现延迟任务的话,还是可取的。
几乎所有的 MQ 中间件都可以实现延迟任务,在这里更准确的叫法应该叫延队列。本文就使用 RabbitMQ 为例,来看它是如何实现延迟任务的。
RabbitMQ 实现延迟队列的方式有两种:
通过消息过期后进入死信交换器,再由交换器转发到延迟消费队列,实现延迟功能;
使用 rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange 插件实现延迟功能。
由于使用死信交换器比较麻烦,所以推荐使用第二种实现方式 rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange 插件的方式实现延迟队列的功能。
首先,我们需要下载并安装 rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange 插件,下载地址:http://www.rabbitmq.com/community-plugins.html
选择相应的对应的版本进行下载,然后拷贝到 RabbitMQ 服务器目录,使用命令 rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange 开启插件,在使用命令 rabbitmq-plugins list 查询安装的所有插件,安装成功如下图所示:
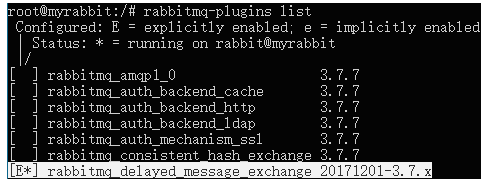
最后重启 RabbitMQ 服务,使插件生效。
首先,我们先要配置消息队列,实现代码如下:
import com.example.rabbitmq.mq.DirectConfig;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;@Configuration
public class DelayedConfig {final static String QUEUE_NAME = "delayed.goods.order";final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "delayedec";@Beanpublic Queue queue() {return new Queue(DelayedConfig.QUEUE_NAME);}// 配置默认的交换机@BeanCustomExchange customExchange() {Map args = new HashMap<>();args.put("x-delayed-type", "direct");//参数二为类型:必须是x-delayed-messagereturn new CustomExchange(DelayedConfig.EXCHANGE_NAME, "x-delayed-message", true, false, args);}// 绑定队列到交换器@BeanBinding binding(Queue queue, CustomExchange exchange) {return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with(DelayedConfig.QUEUE_NAME).noargs();}
} 然后添加增加消息的代码,具体实现如下:
import org.springframework.amqp.AmqpException;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessagePostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;@Component
public class DelayedSender {@Autowiredprivate AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;public void send(String msg) {SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");System.out.println("发送时间:" + sf.format(new Date()));rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(DelayedConfig.EXCHANGE_NAME, DelayedConfig.QUEUE_NAME, msg, new MessagePostProcessor() {@Overridepublic Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException {message.getMessageProperties().setHeader("x-delay", 3000);return message;}});}
}再添加消费消息的代码:
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "delayed.goods.order")
public class DelayedReceiver {@RabbitHandlerpublic void process(String msg) {SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");System.out.println("接收时间:" + sdf.format(new Date()));System.out.println("消息内容:" + msg);}
}最后,我们使用代码测试一下:
import com.example.rabbitmq.RabbitmqApplication;
import com.example.rabbitmq.mq.delayed.DelayedSender;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class DelayedTest {@Autowiredprivate DelayedSender sender;@Testpublic void Test() throws InterruptedException {SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");sender.send("Hi Admin.");Thread.sleep(5 * 1000); //等待接收程序执行之后,再退出测试}
}以上程序的执行结果如下:
发送时间:2020-04-13 20:47:51
接收时间:2020-04-13 20:47:54
消息内容:Hi Admin.
从结果可以看出,以上程序执行符合延迟任务的实现预期。
